Last year's 12th generation Core Alder Lake pioneered the x86 high-performance hybrid architecture. Compared with previous products, the processor architecture is an earth shaking change, and the performance is also greatly improved compared with the 11th generation Core. At the same time, PCI-E 5.0 and DDR5 memory are introduced into the consumer market. A year later, Intel launched its successor, the 13th generation Core Processor Raptor Lake. It has greatly improved the response speed of P-Core on the basis of Alder Lake, and increased the number of E-Core, which has greatly improved the multithreading performance of the processor. Of course, it is also facing a more powerful competitor, the Zen-4 architecture Reelon 7000 series.
13 Generation Core Processor Raptor Lake Changes
Different from the huge change when the 11th generation of Core upgraded to the 12th generation last year, this year's 13th generation of Core can actually be said to be improved on the 12th generation of Core. The degree of change is relatively small. The areas of improvement include more E-Core, higher frequency due to process improvement, increased L2 cache, and improved hardware thread scheduler.
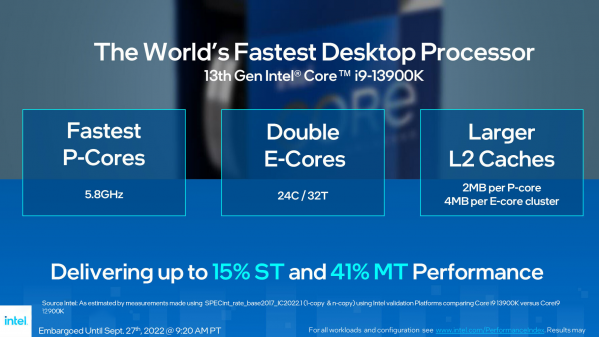
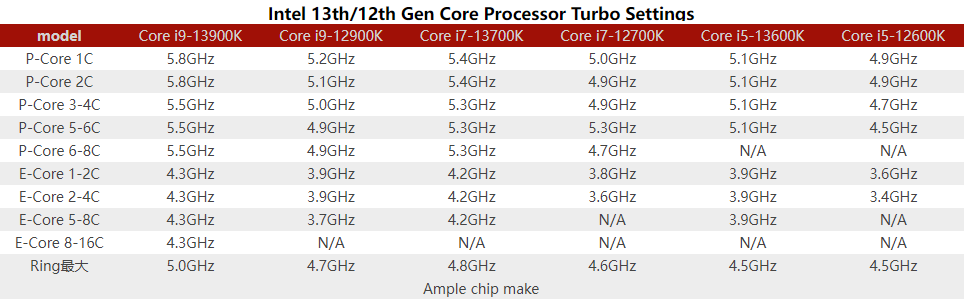
The number of P-Cores of the 13th generation Core processors has not changed. Like the previous generation, the maximum number of P-Cores is 8, but the maximum frequency is increased to 5.8GHz, 600 MHz more than the Core i9-12900K, and 300 MHz more than the Core i9-12900KS. The number of E-Cores has doubled from 8 to 16, and can have up to 32 threads of 8P+16E. In addition, the L2 cache of the P-Core has increased from 1.25 MB to 2 MB, and the L2 cache of the E-Core has increased from 2 MB to 4 MB, Many improved 13 generation Core processors can bring up to 15% single thread and 41% multithreading performance improvement.
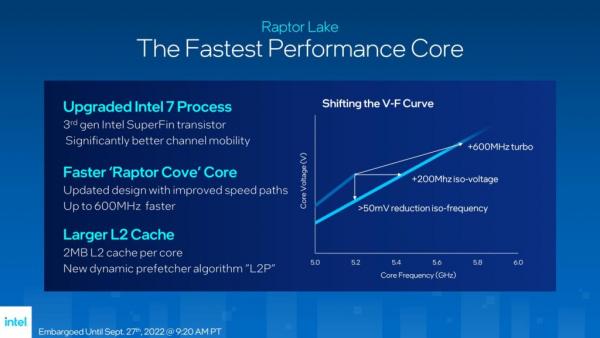
The Raptor Lake processor adopts the improved Intel 7 manufacturing process, which has significantly improved the channel mobility. Compared with the manufacturing process adopted by Alder Lake, it has significantly improved the optimized new manufacturing process.
P-Core adopts Raptor Cove architecture. Thanks to the improved process, it can obtain the same frequency as Golden Cove at a lower voltage. Also at 5.2GHz, the core voltage is 50mV lower, and the frequency can be increased by 200MHz at the same voltage. At the same time, the highest frequency is further increased by 500MHz, up to 5.8GHz. This optimized voltage and frequency curve will allow Raptor Lake to perform better on low-voltage notebook processors.
Raptor Cove's L2 cache capacity has been increased from 1.25MB to 2MB, and a new dynamic prefetching method is adopted, which uses machine learning for real-time data telemetry to achieve more accurate prefetching.
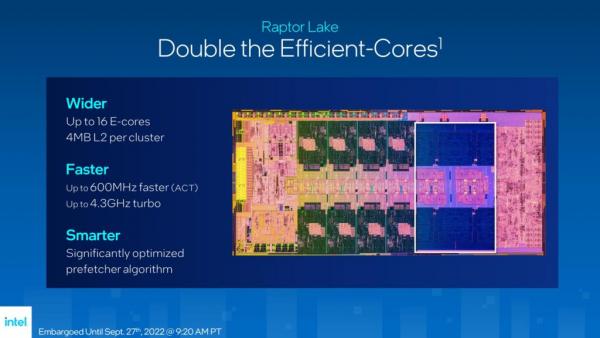
E-Core still maintains the Grace Mont architecture, but the number of cores has doubled, up to 16 cores, the L2 cache capacity shared by each group has also doubled to 4MB, and the frequency has also been increased to a maximum of 4.3GHz. Now E-Core Both in terms of IPC and frequency, it has surpassed the original Skylake processor, with better performance and lower power consumption, with a very good energy consumption ratio. And E-Core also improved the prefetch algorithm, achieving a 7% performance improvement.
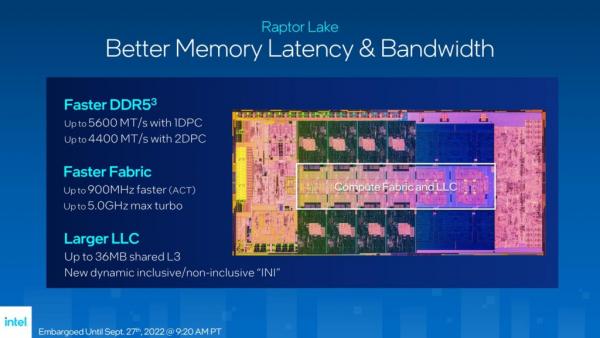
The L3 cache capacity has increased to 36MB. The new intelligent cache has two modes: dynamic inclusion and non inclusion. The containment mode places all MOC data in an intelligent cache, so it is more optimal for improving the performance of a single thread; The non containment mode selectively puts MOC data into the cache, which can optimize the performance of multithreading. Raptor Lake can set intelligent cache mode through dynamic strategy, and set applicable inclusive or non inclusive mode according to various application scenarios.
The frequency of the ring bus has also been further improved. Compared with the previous generation, the maximum increase is 900MHz. Now the ring bus frequency can reach 5GHz, which helps to further improve these improvements. All of these improvements reduce the delay of the entire data reading, and greatly benefit application scenarios such as games.
Raptor Lake's 15% single-threaded performance improvement is mostly brought about by the frequency increase, cache and memory improvements have a small impact, while the 41% multi-threaded performance improvement is caused by the increase in the number of cores, frequency increase and cache capacity increase. Factors play a major role, and memory improvements also have a small effect.
If the power consumption of the Core i9-13900K is adjusted to 241W, which is the same as that of the Core i9-12900K, the performance is still 37% ahead. If the power consumption is adjusted to 115W, the performance is still 21% higher than that of the Core i9-13900K. Even the Core i9-13900K only needs 65W of power consumption to give play to the same multithreading performance of the Core i9-12900K. The performance of Raptor Lake per watt is significantly improved compared with the previous generation.
The new processor has also been further optimized in the Intel hardware thread scheduler, and the thread category boundary has been updated, from the original two levels to four levels, which can better understand the usage of front-end applications and the operation of back-end programs, Windows 11 The 22H2 system has also optimized thread classification.
13th generation Core K series processor specifications list
The starting lineup of the 13th generation Core, including Core i9-13900K/KF, i7-13700K/KF and i5-13600K/KF:
Compatible with Z790 chipset
The 13th generation Core processor has better support for DDR5 memory, and now supports DDR5-5600 memory. The matching 700 series motherboard supports more PCI-E 4.0 channels, and now the Z790 PCH can provide up to 20 PCI-E 4.0, 8 more than the previous generation, the number of available USB 3.2 Gen 2*2 ports has also increased from 4 to 5, and users can also directly use the 13th generation Core processor directly on the existing 600 series motherboard.